|
C.a. Governing equations of the 1D model
|
The potential temperature of the model atmosphere composed of ideal
gas is calculated as follows.
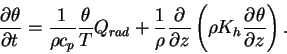 |
(C.1) |
where 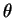 is the potential temperature, is the potential temperature, 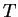 is the temperature, is the temperature, 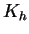 is
the vertical diffusion coefficient, is
the vertical diffusion coefficient, 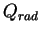 is the radiative
heating rate per unit mass, is the radiative
heating rate per unit mass,
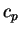 is the specific heat of constant pressure
per unit mass is the specific heat of constant pressure
per unit mass
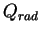 is calculated by
convergence of the radiative heat flux obtained by
radiative transfer equation of
CO2 (see
appendix A.d.i ).
The radiative transfer associated with dust is not considered.
The second term in right hand side represents the heat transport owing
to thermal convection which is parameterized as the vertical
diffusion.
is calculated by
convergence of the radiative heat flux obtained by
radiative transfer equation of
CO2 (see
appendix A.d.i ).
The radiative transfer associated with dust is not considered.
The second term in right hand side represents the heat transport owing
to thermal convection which is parameterized as the vertical
diffusion.
The vertical structure of model atmosphere is given by the hydrostatic equation.
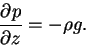 |
(C.2) |
The vertical diffusion coefficient 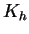 is calculated
as follows (Gierasch and Goody, 1968). is calculated
as follows (Gierasch and Goody, 1968).
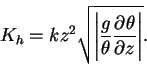 |
(C.3) |
where 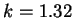 (Priestley, 1959).
(Priestley, 1959).
The sensible heat flux 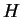 is calculated as follows
(Gierasch and Goody, 1968). is calculated as follows
(Gierasch and Goody, 1968).
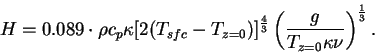 |
(C.4) |
where 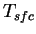 is the surface temperature, is the surface temperature, 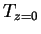 is the surface atmospheric temperature. is the surface atmospheric temperature.
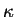 is the atmospheric thermal diffusion
coefficient, is the atmospheric thermal diffusion
coefficient, 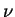 is the atmospheric kinematic viscosity,
The values of is the atmospheric kinematic viscosity,
The values of 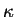 and and 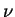 are
8×10-4
m2sec-1
and
1×10-3
m2sec-1
(Gierasch and Goody, 1968).
The sensible heat flux are
8×10-4
m2sec-1
and
1×10-3
m2sec-1
(Gierasch and Goody, 1968).
The sensible heat flux 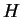 is 0 when the surface
atmospheric temperature is larger than
the surface temperature. is 0 when the surface
atmospheric temperature is larger than
the surface temperature.
The surface temperature 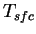 is calcuated by using the
thermal diffusion equation (see appendix A.e ). is calcuated by using the
thermal diffusion equation (see appendix A.e ).
|