|
A.d.i. Radiative transfer of atmospheric CO2
|
Both infrared and near infrared radiative flux associated with
CO2 are calculated by Goody narrow band
model (c.f., Goody and Young, 1989).
By using the band model, the temperature profile around 10 ∼ 15 km height
which is correspond to tropopause region in the dust-free Martian
atmosphere can be calculated precisely.
In calculating infrared radiative flux, CO2
15 μm band is only considered.
The upward and downward infrared radiative flux ( 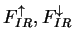 )
and the infrared radiative heating rate per unit mass )
and the infrared radiative heating rate per unit mass 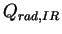 are calculated as follows. are calculated as follows.
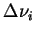 is the ith narrow band width and is the ith narrow band width and
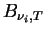 is the Plank function which is
represented as follows. is the Plank function which is
represented as follows.
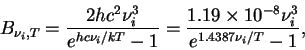 |
(A.26) |
where 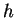 is the Plank constant, is the Plank constant, 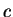 is
speed of light, is
speed of light, 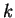 is the Boltzmann constant, and is the Boltzmann constant, and
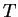 is temperature. is temperature.
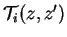 is the transmission function averaged over is the transmission function averaged over
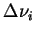 around around 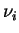 . .
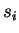 is line strength, is line strength, 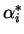 is
square root of the product of line strength and line width and is
square root of the product of line strength and line width and 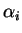 is the reference value of is the reference value of 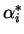 , ,
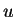 is effective path length, and is effective path length, and 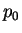 is reference pressure (= 1013 hPa). is reference pressure (= 1013 hPa).
In calculating near infrared solar radiative flux,
CO2 4.3 μm, 2.7 μm, and 2.0
μm band are considered.
The near infrared solar radiative flux 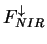 and
the near infrared radiative heating rate per unit mass and
the near infrared radiative heating rate per unit mass
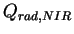 are calculated as follows. are calculated as follows.
where 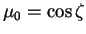 , , 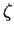 is the solar
zenith angle, and is the solar
zenith angle, and 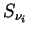 is the solar radiative flux
per unit wave length at the top of atmosphere which is represented
as follows. is the solar radiative flux
per unit wave length at the top of atmosphere which is represented
as follows.
where 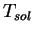 is the surface temperature of the sun (=
5760 K), is the surface temperature of the sun (=
5760 K), 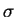 is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant (=
5.67× 10-8
Wm-2K-4, is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant (=
5.67× 10-8
Wm-2K-4,
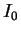 is solar constant on the mean radius of Mars orbit
(= 591 Wm-2), is solar constant on the mean radius of Mars orbit
(= 591 Wm-2), 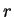 and and
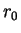 is the radius of Mars orbit and its mean
value, is the radius of Mars orbit and its mean
value, 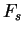 is solar
radiative flux at the top of atmosphere. is solar
radiative flux at the top of atmosphere.
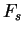 is depend on season, latitude and local
time.
Detail descriptions of is depend on season, latitude and local
time.
Detail descriptions of 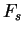 and and 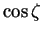 are
shown in appendix A.d.vi. are
shown in appendix A.d.vi.
The transmission function averaged over 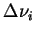 in near
infrared wavelength region is similar to that in infrared
wavelength region except for the effective path length in near
infrared wavelength region is similar to that in infrared
wavelength region except for the effective path length 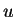 . .
|